Tags
AI, artificial-intelligence, Cloud, LLM, OpAMP, Open Telemetry, OTel, Protobuf, Spec, Technology
Fluent Bit and OpenTelemetry’s Collector (as well as many other observability tools) are designed to use a distributed/agent model for deployment. This model can pose challenges, including ensuring that all agents are operating healthily and correctly configured. This is particularly true outside of a Kubernetes ecosystem. But even within a Kubernetes ecosystem, more than basic insights are required (for example, is it running flat out or over-resourced). Fluent Bit exposes its own metrics and logs so that you can either configure Fluent Bit to forward the metrics and logs to an endpoint (or allow Prometheus to scrape the metrics).
As we’re usually using Fluent Bit to collect data and route it to tools like Prometheus, Grafana, etc., or perhaps a more commercial product. So it makes sense that Fluent Bit is also sharing its own status and health.
When it comes managing the configuration of Fluent Bit, we have lots of options for Kubernetes deployments (from forcing pod replacement, to sharing configurations via persistent volume claims, and Fluent Bit reloading configs), but given that Observability needs to operate on simple virtualized and bare metal scenarios, and not everything can be treated as dynamically replaceable more general strategies such as GITOps and potentially using Istio (yes, there really good use cases for Istio outside of Kubernetes) are available. But there is also more advanced tooling, such as Puppet, Chef, and Ansible.
The challenge is non of these tools provides out-of-the-box capabilities to fully exploit the control surface that OTel Collectors and Fluent Bit offer. So the OpenTelemetry community has elected to develop a new standard called OpAMP, which fits snuggly into the OTel ecosystem.
OpAMP defines an agent/client and server model in which the central server provides control, measurement, etc., to all Collectors. The agent/client side can be deployed in two ways: wired directly into a collector or via a separate supervisor tool. Integrating the client-side directly into the client is great, as it avoids introducing a new local process. The heart of OpAMP is the message exchange, which we’ll look at more in a moment.
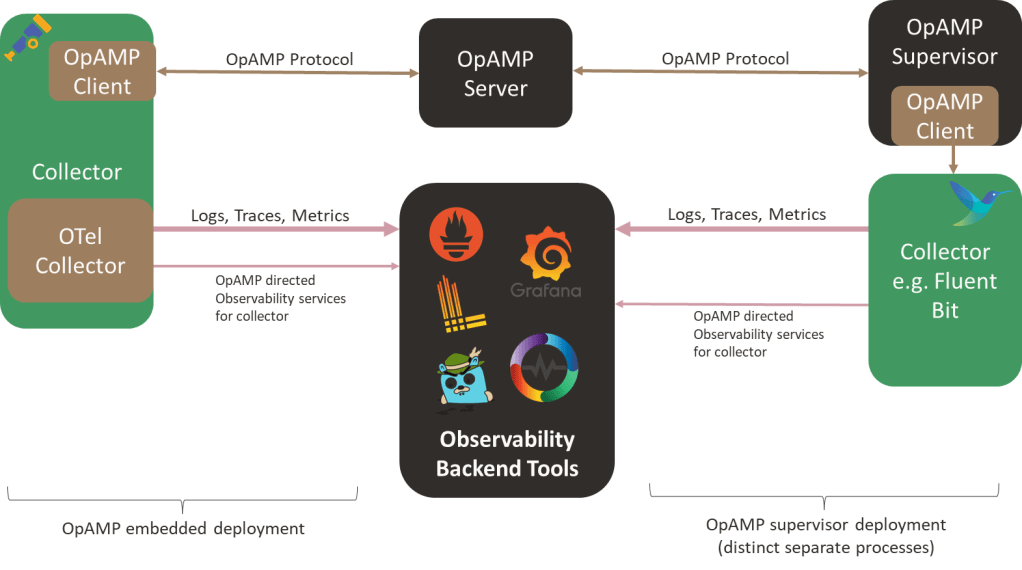
Today, Fluent Bit would need to use the Supervisor model without modification (although GitHub shows a feature request to support the protocol, we haven’t heard whether or when it will be implemented). But it is early days, and some aspects of the protocol are still classified as ‘development’. That said, it is worth looking more closely at OpAMP as it offers some interesting opportunities, particularly around how we could easily evolve ideas such as chatOps.
While I’m not a fan of having a peer process for Fluent Bit, on the basis that we now have two distinct processes to support observability, we could experiment with the supervisor spawning Fluent Bit as a child process, which would let the supervisor easily spot Fluent Bit failing. At the sametime the supervisor can communicate with Fluent Bit using the localhost loopback adapter and the usual APIs.
Understanding the OpAMP Protocol and what it offers
Lets start with what the OpAMP protocol offers, firstly very little of it is mandatory (this is both good and bad – it means we can build compatibility in a more incremental manner, if certain behaviours are provided elsewhere, then the agent doesn’t have to offer a capability it is also tolerant of what an agent or collector can and can’t do):
- Heatbeat and announce the agent’s existence to the server, along with what the agent is capable of/allowed to do regarding OpAMP features.
- Status information, including:
- environmental information
- configuration being run
- modules being used
- Perform updates to resources, including:
- Agent configuration
- TLS certificate rotation
- Credentials management
- module or even an entire agent installation
- issuing of custom commands.
- directing the agent’s own telemetry to specific services/endpoints.
The heart of this protocol is the contract between the client (agent/collector) and the server, defined using Protobuf3. This means you can easily create the code skeleton to handle the payload objects, which will be transmitted in binary form (giving network traffic efficiency and the price of not being humanly readable or dynamically processable, insofar as you need to know the Protobuf definition to extract any meaning).
In addition to the Protobuf definitions, there are rules for handling messages, specifying when a message or response is required, message sequence numbering, and the default heartbeat frequency. But there aren’t any complex exchanges involved.
The binary payloads are exchanged over Sockets (allowing full-duplex exchanges where the server can send requests at any time) or over HTTP (providing half-duplex, aka polling/client check-in, at which point the server can respond with an instruction) – a strategy that is becoming increasingly common today.
The benefits we see
Regardless of whether you’re in a Kubernetes environment, the ability to ask agents/collectors to quickly tweak their configuration is attractive. If you start suspecting a service or application is not behaving as expected, if Fluent Bit is filtering your logs or sampling traces, you can quickly push a config change out to allow more through, providing further insight into what is going on – you don’t need to wait for a Kubernetes scheduler to roll through with replacing pods.
With the rise of AI, having a central point of contact makes it easier to wrap a central server as an MCP tool and have a natural language command interface. Along with the possibility that you can potentially send custom commands to the agent (or supervisor) to initiate a task. This was part of the functionality we effectively implemented in our original chatops showcase. The problem was that in the original solution, we deployed a small Slack bot that directed HTTP calls to Fluent Bit. With the OpAMP framework, we can direct the request to the server, which will route the command to the correct Fluent Bit node through a more trustworthy channel.
Implementation
The OpAMP protocol is likely to be widely adopted by commercial service providers (Bindplane, OneUpTime, for example), as it allows them to start working with additional agents/collectors that are already deployed (for example, a supervisor could be used to manage a Fluentd fleet, where there isnt the appetite to refactor all the configuration to Fluent Bit or an OTel Collector). Furthermore, it has the potential to simplify by standardizing functionality.
In terms of resource richness in the OpenTelemetry GitHub repo, I suspect (and hope) there will be more to come (a UI and richer details on how a base server can be extended, for example). At the time of writing, within the OpenTelemetry GitHub repository, we can see:
- The published spec
- Go implementation of the protocol: the server accepts and responds to messages, and the client includes some test functionality to populate messages.
- A supervisor implementation that, through configuration, can be pointed at an agent to observe, and the configuration so that the supervisor is uniquely identifiable to the server. This is also implemented in Go.
- Open Telemetry Collector extension






You must be logged in to post a comment.